Telegram Group »
India »
Volcanscientific : when Volcano science meets Telegram - Die Wissenschaft der Vulkane - La ciencia de los volcanes »
Telegram Webview »
Post 34
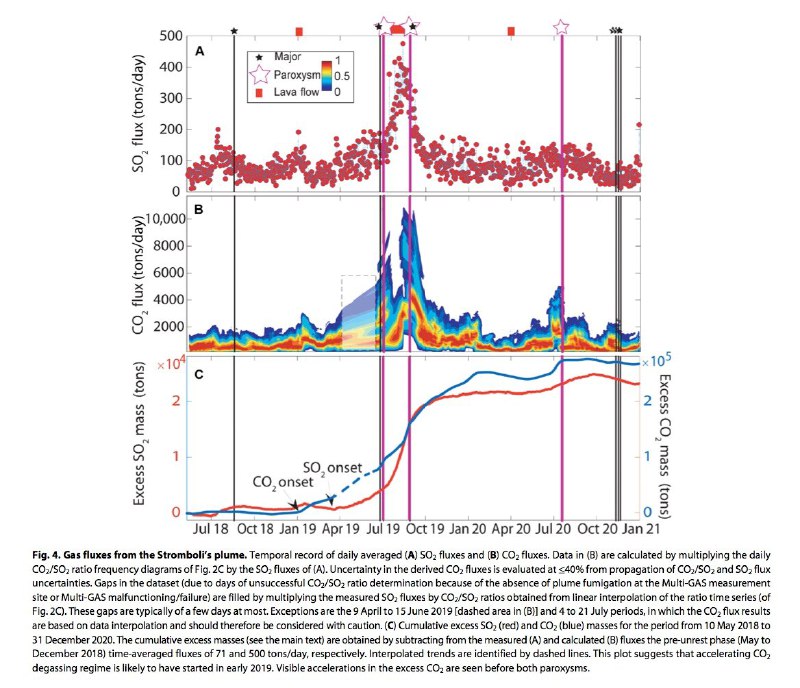
The fluctuations in plume CO2/SO2 ratios at Stromboli reflect temporal changes in the relative gas contributions from the deep (CO2-rich) and shallow (CO2-poor and SO2-rich) magma storage zones (53). Hence, a high CO2/SO2 ratio does not necessarily imply an elevated deep gas flux and, instead, can also derive from a reduced level of shallow magma degassing. For example, we propose that a reduced SO2 contribution from shallow conduit magma is likely to have caused the ~4-month-long (September to December 2019) period of high CO2/SO2 ratios following the 2019 unrest, as supported by concurrent stable, low SO2 concentrations (Fig. 2A) and declining SO2 fluxes (Fig. 4A).
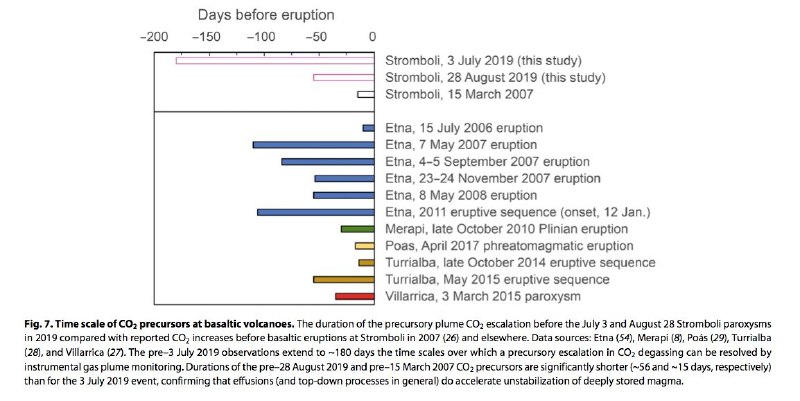
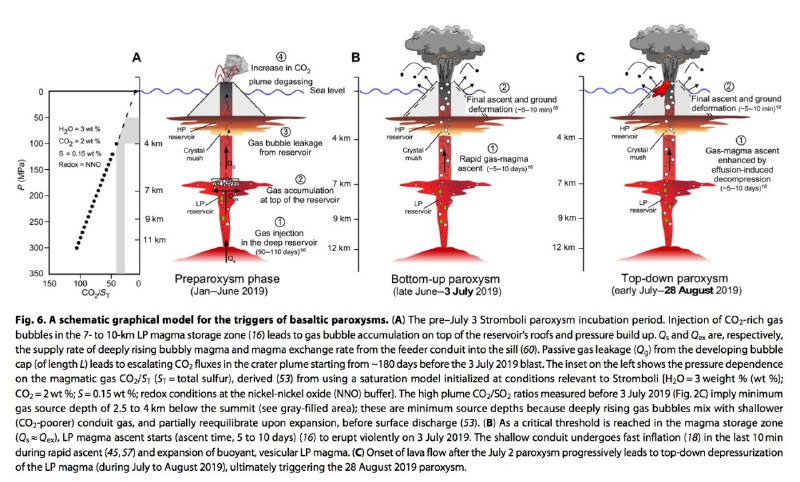
To unequivocally identify periods associated with heightened deep CO2 release, we rely on our CO2 flux record (Figs. 4B and 5). This time series highlights, unambiguously, that a surge of deep CO2 gas is associated with Stromboli’s unrest during summer 2019, with daily CO2 fluxes peaking at a factor of ~4 above typical background values (<1000 tons/day) before both blasts. Our results provide compelling evidence that volcanic CO2 flux is an effective tracer of deep degassing, thus supporting previous work at Etna (21, 32, 54), Villarrica (27), Turrialba (28), and Poás (29), where elevated fluxes of deep-derived volatiles have been shown to precede paroxysmal eruptions of basaltic magma.
We note that the 2014 effusive unrest—the only post-2000 event not associated with a paroxysmal explosion—is consistently charac- terized by the lowest excess CO2 degassing budget (Fig. 8). Therefore, it appears that in 2014, the effusion had less of an impact on the deep plumbing system than in 2007 and 2019. It is possible that Stromboli’s deep reservoir experienced decompression in 2014, too, but the volume of CO2 gas involved was sufficiently low to preclude the unrest culminating into a paroxysm. Lower effusion-driven magma decompression rates in 2014 (8.4 Pa/s), relative to 2007 (29.3 Pa/s), may have been responsible for the reduced levels of CO2 degassing.
To unequivocally identify periods associated with heightened deep CO2 release, we rely on our CO2 flux record (Figs. 4B and 5). This time series highlights, unambiguously, that a surge of deep CO2 gas is associated with Stromboli’s unrest during summer 2019, with daily CO2 fluxes peaking at a factor of ~4 above typical background values (<1000 tons/day) before both blasts. Our results provide compelling evidence that volcanic CO2 flux is an effective tracer of deep degassing, thus supporting previous work at Etna (21, 32, 54), Villarrica (27), Turrialba (28), and Poás (29), where elevated fluxes of deep-derived volatiles have been shown to precede paroxysmal eruptions of basaltic magma.
We note that the 2014 effusive unrest—the only post-2000 event not associated with a paroxysmal explosion—is consistently charac- terized by the lowest excess CO2 degassing budget (Fig. 8). Therefore, it appears that in 2014, the effusion had less of an impact on the deep plumbing system than in 2007 and 2019. It is possible that Stromboli’s deep reservoir experienced decompression in 2014, too, but the volume of CO2 gas involved was sufficiently low to preclude the unrest culminating into a paroxysm. Lower effusion-driven magma decompression rates in 2014 (8.4 Pa/s), relative to 2007 (29.3 Pa/s), may have been responsible for the reduced levels of CO2 degassing.
group-telegram.com/Volcanscientific/34
Create:
Last Update:
Last Update:
The fluctuations in plume CO2/SO2 ratios at Stromboli reflect temporal changes in the relative gas contributions from the deep (CO2-rich) and shallow (CO2-poor and SO2-rich) magma storage zones (53). Hence, a high CO2/SO2 ratio does not necessarily imply an elevated deep gas flux and, instead, can also derive from a reduced level of shallow magma degassing. For example, we propose that a reduced SO2 contribution from shallow conduit magma is likely to have caused the ~4-month-long (September to December 2019) period of high CO2/SO2 ratios following the 2019 unrest, as supported by concurrent stable, low SO2 concentrations (Fig. 2A) and declining SO2 fluxes (Fig. 4A).
To unequivocally identify periods associated with heightened deep CO2 release, we rely on our CO2 flux record (Figs. 4B and 5). This time series highlights, unambiguously, that a surge of deep CO2 gas is associated with Stromboli’s unrest during summer 2019, with daily CO2 fluxes peaking at a factor of ~4 above typical background values (<1000 tons/day) before both blasts. Our results provide compelling evidence that volcanic CO2 flux is an effective tracer of deep degassing, thus supporting previous work at Etna (21, 32, 54), Villarrica (27), Turrialba (28), and Poás (29), where elevated fluxes of deep-derived volatiles have been shown to precede paroxysmal eruptions of basaltic magma.
We note that the 2014 effusive unrest—the only post-2000 event not associated with a paroxysmal explosion—is consistently charac- terized by the lowest excess CO2 degassing budget (Fig. 8). Therefore, it appears that in 2014, the effusion had less of an impact on the deep plumbing system than in 2007 and 2019. It is possible that Stromboli’s deep reservoir experienced decompression in 2014, too, but the volume of CO2 gas involved was sufficiently low to preclude the unrest culminating into a paroxysm. Lower effusion-driven magma decompression rates in 2014 (8.4 Pa/s), relative to 2007 (29.3 Pa/s), may have been responsible for the reduced levels of CO2 degassing.
To unequivocally identify periods associated with heightened deep CO2 release, we rely on our CO2 flux record (Figs. 4B and 5). This time series highlights, unambiguously, that a surge of deep CO2 gas is associated with Stromboli’s unrest during summer 2019, with daily CO2 fluxes peaking at a factor of ~4 above typical background values (<1000 tons/day) before both blasts. Our results provide compelling evidence that volcanic CO2 flux is an effective tracer of deep degassing, thus supporting previous work at Etna (21, 32, 54), Villarrica (27), Turrialba (28), and Poás (29), where elevated fluxes of deep-derived volatiles have been shown to precede paroxysmal eruptions of basaltic magma.
We note that the 2014 effusive unrest—the only post-2000 event not associated with a paroxysmal explosion—is consistently charac- terized by the lowest excess CO2 degassing budget (Fig. 8). Therefore, it appears that in 2014, the effusion had less of an impact on the deep plumbing system than in 2007 and 2019. It is possible that Stromboli’s deep reservoir experienced decompression in 2014, too, but the volume of CO2 gas involved was sufficiently low to preclude the unrest culminating into a paroxysm. Lower effusion-driven magma decompression rates in 2014 (8.4 Pa/s), relative to 2007 (29.3 Pa/s), may have been responsible for the reduced levels of CO2 degassing.
BY Volcanscientific : when Volcano science meets Telegram - Die Wissenschaft der Vulkane - La ciencia de los volcanes

Share with your friend now:
group-telegram.com/Volcanscientific/34
